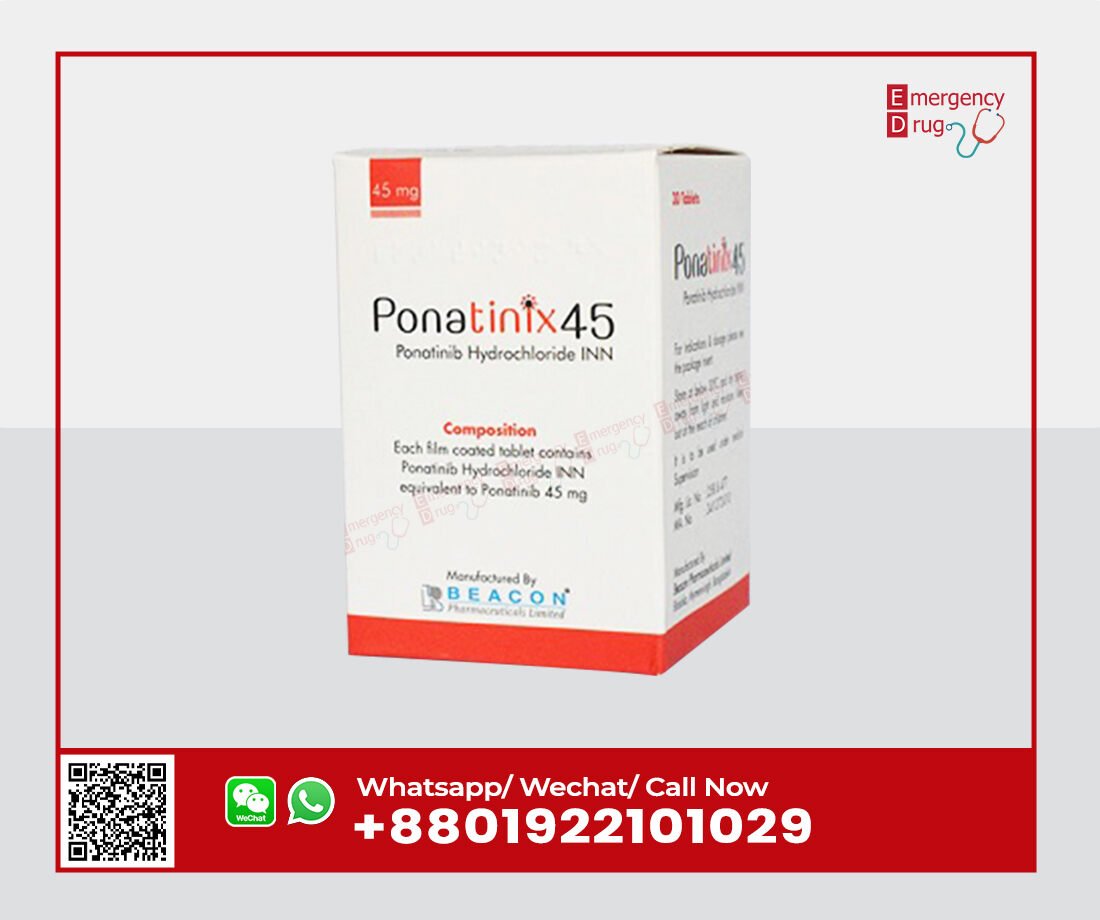
Ponatinix (Ponatinib) 45 MG – 30 Tablets
Price: $685.00
Product Feature:
| Manufacturer | : Beacon Pharma Ltd |
| Indication | : Chronic lymphocytic leukemia |
| Strength | : 45 mg |
| Quantity | : 30 Tablets |
| Storage | : Below 30°C |
| Registrations | : Export Only |


Description
Ponatinix (Ponatinib), generic is a prescription Tablets use to treat of blood cancer which is chronic phase, accelerated phase, or blast phase chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) or Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL) for whom no other tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) medicines are received. Ponatinix manufactured by Beacon Pharma Ltd. in Bangladesh.
Indications
Ponatinib is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the:
Adult patients with chronic phase, accelerated phase, or blast phase chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) or Ph+ ALL for whom no other tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy is indicated.
Patients with T315I-positive CML (chronic phase, accelerated phase, or blast phase) or T315I-positive Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL).
Pharmacology Ponatinib
Ponatinib inhibited the in vitro tyrosine kinase activity of ABL and T315I mutant ABL with IC 50 concentrations of 0.4 nM and 2.0 nM, respectively. In vitro, activity of additional kinases with IC 50 concentrations between 0.1 nM and 20 nM, including members of the VEGFR, PDGFR, FGFR, EPH receptors and SRC families of kinases, and KIT, RET, TIE2, and FLT3. There is viability of cells expressing native or mutant BCR-ABL, including T315I. In mice, treatment with ponatinib reduce the size of tumors expressing native or T315I mutant BCR-ABL when compared to controls.
Dosage & Administration Ponatinib
Recommended dose: 45 mg taken orally once daily with or without food
Hepatic Impairment: 30 mg orally once daily. Modify or interrupt dosing for hematologic and non-hematologic toxicity.
Side Effects
The most common non-hematologic adverse reactions (≥20%) were, abdominal pain, rash, constipation, headache, dry skin, arterial occlusion, fatigue, hypertension, pyrexia, arthralgia, nausea, diarrhea, lipase increased, vomiting, myalgia and pain in extremity.
Pregnancy & Lactation
In animals, it cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on Ponatinib use in pregnant women. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of ponatinib to pregnant rats during organogenesis caused adverse developmental effects. At doses lower than human exposures at the recommended human dose. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
There is no data on the presence of ponatinib in human milk. The effects on the breastfed infant or on milk production.
Use in Special Populations
Storage Conditions
For more Oncology medicine, visit our SHOP









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.