Description
Elopag 50 mg is an orally bioavailable, small-molecule TPO-receptor agonist that reaction with the transmembrane domain of the human TPO-receptor and initiates signaling cascades that induce proliferation and differentiation from bone marrow progenitor cells.
Product Features:
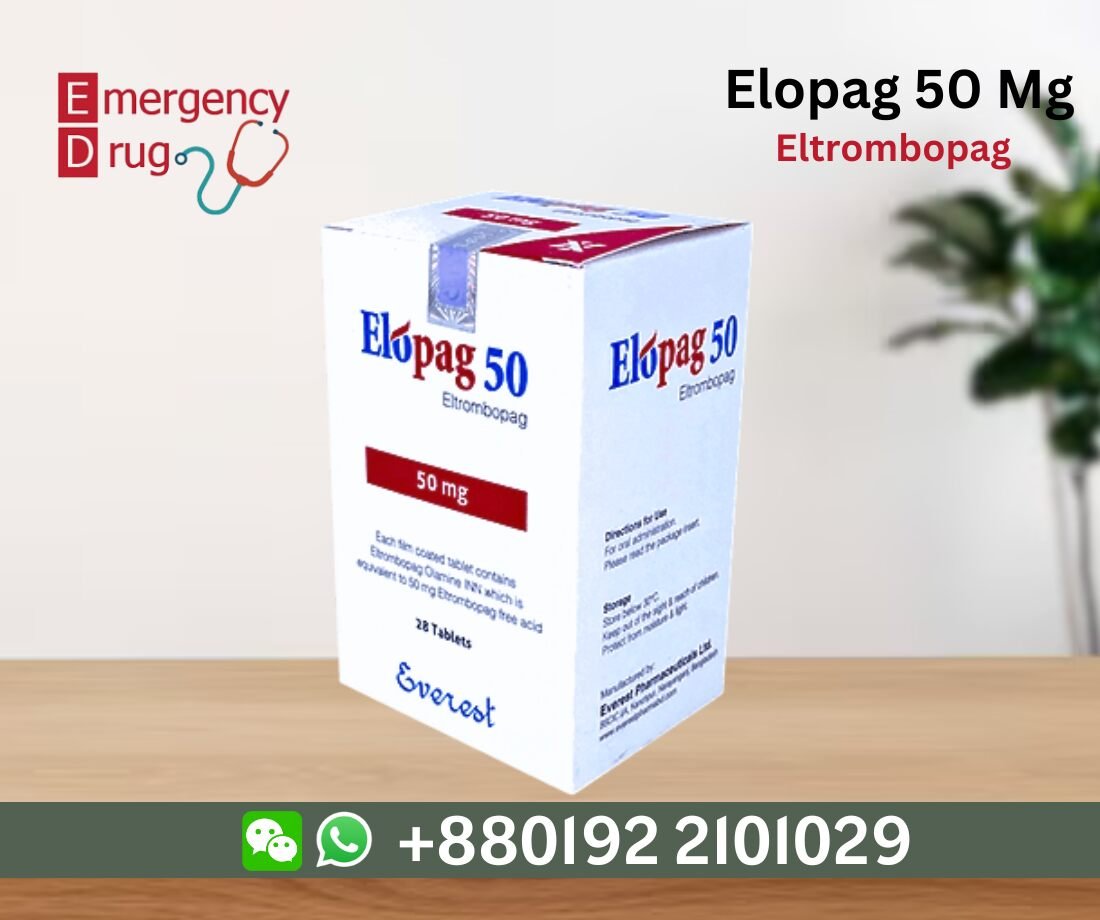
| Product Name | : Elopag |
| Generic Name | : Eltrombopag |
| Manufacturer | : Everest Pharma Ltd |
| Indication | : Low blood platelet counts |
| Formulation | : Tablet |
| Strength | : 50 mg |
| Quantity | : 28 Tablets |
| Storage | : Below 30° |
| Registrations | : Export Only |
Working Principle
Uses
Elopag 50 mg (Eltrombopag) is used for low platelet count due to ITP or HCV infection. That treat low platelet count due to chronic immune (idiopathic), thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) or chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Eltrombopag is also used to treat severe aplastic anemia.
Side Effects
Nausea, Diarrhoea, Upper respiratory tract infection, Vomiting, Increased liver enzymes, Muscle pain, Urinary tract infection.
Thrombocytopenia
A condition in which there is a lower-than-normal number of platelets in the blood. It may result in easy bruising and excessive bleeding from wounds or bleeding in mucous membranes and other tissues.
Platelets (thrombocytes) are colorless blood cells that help blood clot. Platelets stop bleeding by clumping and forming plugs in blood vessel injuries.
A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. One common definition of thrombocytopenia requiring emergency treatment is a platelet count below 50,000 per microliter.
Signs and Symptoms
Thrombocytopenia signs and symptoms may include:
- Easy or excessive bruising (purpura).
- Superficial bleeding into the skin that appears as a rash of pinpoint-sized reddish-purple spots (petechiae), usually on the lower legs.
- Prolonged bleeding from cuts.
- Bleeding from your gums or nose.
- Blood in urine or stools.
- Unusually heavy menstrual flows.
- Fatigue.
- Enlarged spleen.
- Jaundice.
Causes
Thrombocytopenia caused due to:
1. Increase platelet destruction due to reason-
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP).
- Sulfonamide antibiotics (Carbamazepine, Digoxin).
- Heparin.
- Severe trauma.
2. Decrease platelet production due to reason –
- Chemotherapy.
- Viral infection (HCV, HIV).
- Aplastic anemia.
- Bone marrow cancer.
- Long term alcohol intake.
For more Oncology medicine, visit our SHOP







Jose Davila –
Excellent service, they are always responsive and respectful, highly recommended.