Description
Neratinib (Hernix) is an oral, irreversible tyrosine kinase inhibitor. This is the only product in the world approved for intensive adjuvant therapy. After treatment with HER2-positive breast cancer, trastuzumab (Herceptin) reduces the risk of recurrence. The applicable population is to complete the standard trastuzumab adjuvant treatment of patients with undeveloped disease but high-risk factors.
Product Features
| Product Name | : | Hernix |
| Generic Name | : | Neratinib |
| Formulation | : | Tablet |
| Available Pack Size | : | 180’s Pot |
| Available Strength | : | 40 mg |
| Manufacturer | : | Beacon Pharma Ltd |
Hernix 40 MG Price: $1155.00
Indications Neratinib
Breast cancer for women patients completed standard trastuzumab (Herceptin, Herceptin) adjuvant therapy, disease progression, but high-risk factors
Pharmacology Neratinib
Neratinib is a kinase inhibitor that irreversibly binds to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR), Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2), and HER4. Hernix reduces EGFR and HER2 autophosphorylation, downstream MAPK, and AKT signaling pathways. Therefore show antitumor activity in EGFR and/or HER2 expressing carcinoma cell lines. Neratinib human metabolites M3, M6, M7, and M11 inhibited the activity of EGFR, HER2, and HER4 in vitro. In vivo, oral administration of Hernix inhibited tumor growth in mouse xenograft models with tumor cell lines expressing HER2 and EGFR.
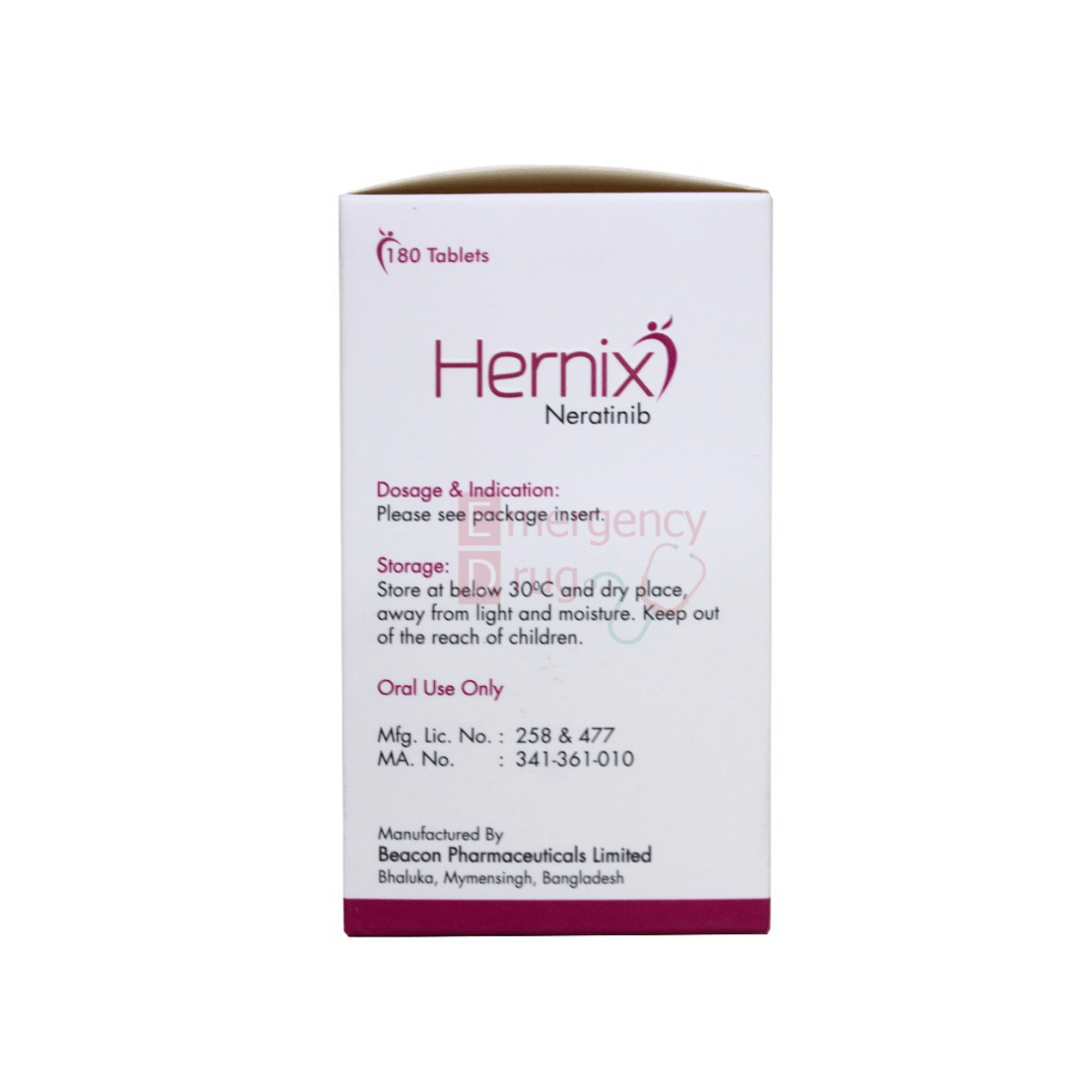
Dosage & Administration
Antidiarrheal prophylaxis: Initiate loperamide with the first dose of Neratinib and continue during the first 2 cycles (56 days) of treatment. Instruct patients to maintain 1-2 bowel movements per day and on how to use antidiarrheal treatment regimens.
Recommended dose: 240 mg (6 tablets) given orally once daily with food for one year. Dose interruptions and/or dose reductions are recommended based on individual safety and tolerability.
Hepatic Impairment: Reduce starting dose to 80 mg in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
Interaction
Gastric acid reducing agents: Avoid concomitant use with proton pump inhibitors (PPI) and H2-receptor antagonists. Separate Hernix by 3 hours after antacid dosing.
Strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use.
Strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers: Safe from concomitant use.
P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrates: Monitor for adverse reactions of narrow therapeutic agents that are P-gp substrates when used concomitantly with Hernix.
Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions (> 5%) were diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, fatigue, vomiting, rash, stomatitis, decreased appetite, muscle spasms, dyspepsia, AST or ALT increase, nail disorder, dry skin, abdominal distention, weight decreased and urinary tract infection.
Pregnancy & Lactation
There are no available data on pregnant women to inform the drug-associated risk. No data are available regarding the presence of neratinib or its metabolites. In human milk or its effects on the breastfed infant or milk production.
Precautions & Warnings
Diarrhea: Aggressively manage diarrhea despite recommended prophylaxis with additional antidiarrheals, fluids, and electrolytes as clinically indicated. Withhold Medicine in patients experiencing severe and/or persistent diarrhea. Permanently discontinue Tablets in patients experiencing Grade 4 diarrhea or Grade ≥ 2 diarrhea after maximal dose reduction.
Hepatotoxicity: Monitor liver function tests monthly for the first 3 months of treatment. Then every 3 months while on treatment and as clinically indicated. Withhold Neratinib in patients experiencing Grade 3 liver abnormalities and permanently discontinue Capsule in patients experiencing Grade 4 liver abnormalities.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: It can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of the potential risks to a fetus and to use effective contraception.
For more Oncology medicine, visit our SHOP





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.