Description
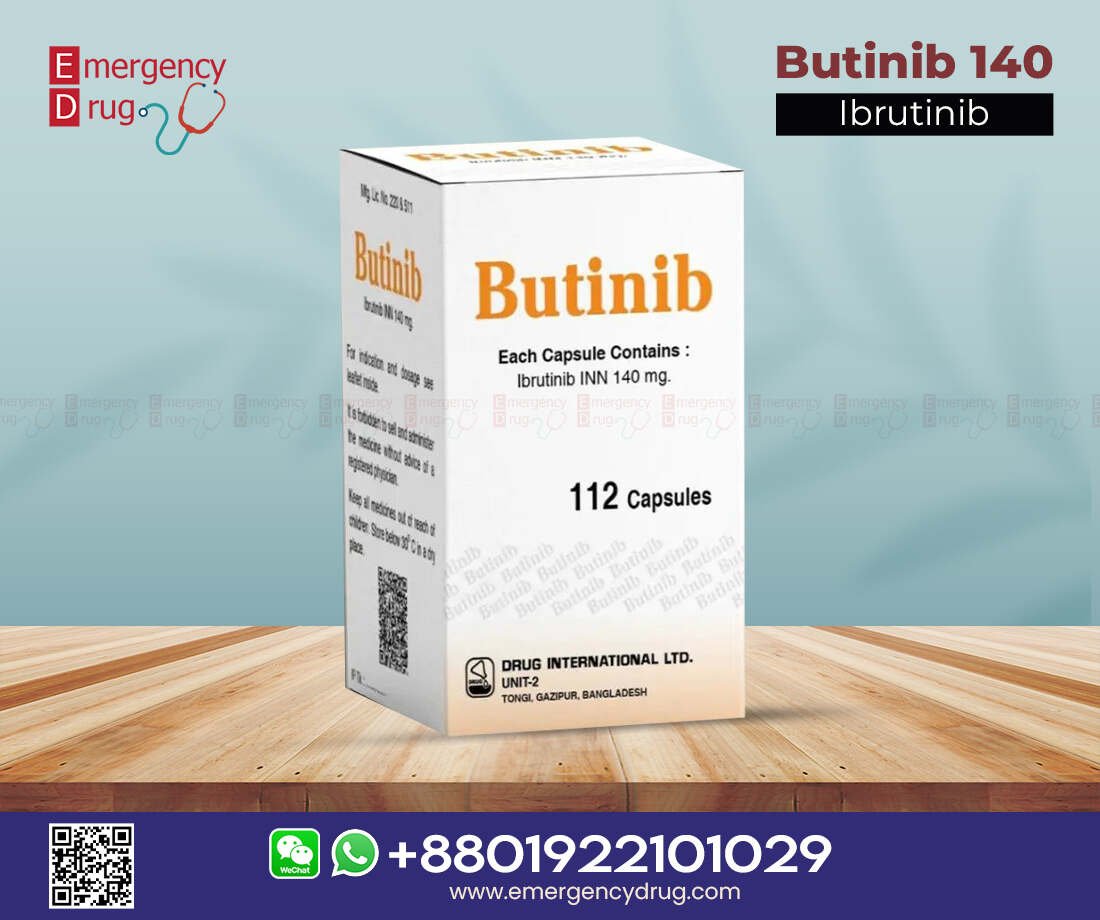
Product Features of Butinib 140 mg:
| Product Name | : | Butinib |
| Generic Name | : | Ibrutinib |
| Formulation | : | Capsules |
| Available Pack Size | : | 112’s Pot |
| Available Strength | : | 140 mg |
| Registrations | : | Export Only |
Indications
Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Butinib 140 mg is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have received at least one prior therapy. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma. Butinib 140 mg is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL)
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma with 17p Deletion: Butinib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) with 17p deletion. Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia: Butinib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM).
Marginal Zone Lymphoma: Butinib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) who require systemic therapy and have received at least one prior anti-CD20-based therapy.
Dosage and Administration
Mantle Cell Lymphoma and Marginal Zone Lymphoma: The recommended dose of Butinib for MCL and MZL is 560 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma and Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia: The recommended dose of Butinib for CLL/SLL and WM as a single agent, in combination with Rituximab for WM, or in combination with Bendamustine and Rituximab for CLL/SLL is 420 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Administer butitinib before rituximab when given on the same day.
Chronic Graft versus Host Disease: The recommended dose of Butinib for cGVHD is 420 mg orally once daily until cGVHD progression, recurrence of an underlying malignancy, or unacceptable toxicity. When a patient no longer requires therapy for the treatment of cGVHD.
Side Effects of Butinib
- Hemorrhage
- Infections
- Cytopenias
- Cardiac Arrhythmias
- Hypertension
- Second Primary Malignancies
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Contraindication:
Contraindicate in patients with known hypersensitivity to Ibrutinib or any other components of this product.
Use in Pregnancy and Lactation: There are no available data on Butinib use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage. If it is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking Butinib, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
Lactation: There is no information regarding the presence of Ibrutinib or its metabolites in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production.
Contraception:
Females: Females of reproductive potential should be advised to avoid pregnancy while taking Ibrutinib and for up to 1 month after ending treatment. If a patient uses this drug during pregnancy or becomes pregnant while taking it, inform them of the potential hazard to the fetus. Advise men to avoid fathering children while receiving butitinib and for 1 month after the last dose.
Pediatric Use: The safety and effectiveness of drug in pediatric patients has not been established. Pediatric studies have not been completed.
Precautions:
Hemorrhage: Fatal bleeding events have occurred in patients treated with the medicine. Grade 3 or higher bleeding events (intracranial hemorrhage (including subdural hematoma), gastrointestinal bleeding, hematuria, and post procedural hemorrhage) have occurred in 3% of patients, with fatalities occurring in 0.3% of 1,011 patients exposed to Butinib in clinical trials. Bleeding events of any grade, including bruising and petechiae, occurred in 44% of patients treated with Butinib. Butinib may increase the risk of hemorrhage in patients receiving antiplatelet.
Infections:
Fatal and non-fatal infections (including bacterial, viral, or fungal) have occurred with Butinib therapy. Grade 3 or greater infections occurred in 24% of 1,011 patients exposed to Butinib in clinical trials. Cases of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) and Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP) have occurred in patients treated with Butinib. Consider prophylaxis according to the standard of care in patients at risk for opportunistic infections. Monitor and assess patients for fever and infection and treat them appropriately.
- Cytopenias: Treatment-emergent Grade 3 or 4 cytopenias including neutropenia (23%), thrombocytopenia (8%), and anemia (3%) based on laboratory measurements occurred in patients with B-cell malignancies treated with single agent Butinib.
- Cardiac Arrhythmias: Fatal and serious cardiac arrhythmias have occurred with therapy. Grade 3 or greater ventricular tachyarrhythmias occurred in 0.2% of patients, and Grade 3 or greater atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter occurred in 4% of 1,011 patients exposed to Butinib inclinical trials. These events have occurred particularly in patients with cardiac risk factors, hypertension, acute infections, and a previous history of cardiac arrhythmias. Periodically patients should be monitore clinically for cardiac arrhythmias.
- Hypertension: Hypertension has occurred in 12% of 1,011 patients treated with the drug in clinical trials with a median time to onset of 5 months (range, 0.03 to 22 months). Monitor patients for new-onset hypertension or for hypertension that is not adequately controlled after initiation of Butinib. Adjust existing anti-hypertensive medications and/or initiate anti-hypertensive treatment as appropriate.
- Second Primary Malignancies: Other malignancies (9%) including non-skin carcinomas (2%) have occurred in 1,011 patients treated with Butinib in clinical trials. The most frequent second primary malignancy was non-melanoma skin cancer (6%).
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome: Tumor lysis syndrome has been infrequently reported with Butinib therapy. The baseline risk should be assesse and taken appropriate precautions, monitored patients closely and treated as appropriate.
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Butinib can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Women should be advise to avoid becoming pregnant while taking it and for 1 month after cessation of therapy. If a pregnant patient uses this drug or becomes pregnant while taking it. They should be informe about the potential hazard to the fetus.
Overdose:
There is no specific experience in the management of Ibrutinib overdose in patients. Patients should be closely monitore who ingest more than the recommended dosage and provided appropriate supportive treatment.
Storage: Store below 30°C in a dry place, away from sunlight. Keep out of the reach of children.
.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.