Axitinib 5 mg (Axinix) Prescribing Information
Hasan
11 Jan, 2024
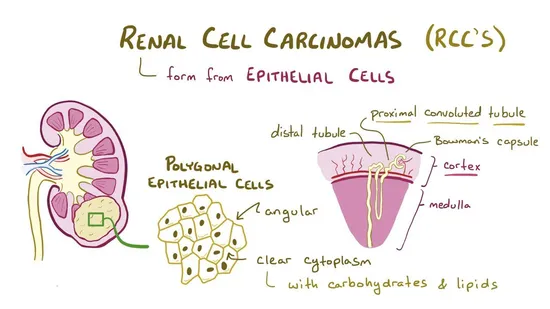

Axitinib is indicated for the treatment of advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) after failure of one prior systemic therapy.
Composition
Axinix 1 mg Tablet: Each film coated tablet contains Axitinib INN 1 mg.
Axinix 5 mg Tablet: Each film coated tablet contains Axitinib INN 5 mg.
Table of Contents
Mechanism of Action
Axitinib drug works by blocking certain proteins called receptor tyrosine kinases, including those known as VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, and VEGFR-3. These proteins play a role in abnormal blood vessel formation, tumor growth, and the progression of cancer.
In laboratory studies and mouse models, Axitinib was found to hinder the activity of these receptors, preventing the growth of blood vessels that support tumors. This inhibition of VEGF-mediated processes, such as endothelial cell proliferation and survival, contributes to the drug’s effectiveness in slowing down cancer growth. In mouse models with implanted tumors, Axitinib demonstrated the ability to inhibit both tumor growth and the activation of VEGFR-2.
Pharmacodynamics
Researchers studied the impact of a single 5 mg dose of Axitinib, with and without 400 mg of Ketoconazole, on the QTc interval in a randomized, single-blinded, two-way crossover study involving 35 healthy individuals.
Results showed no significant changes in the average QTc interval (greater than 20 milliseconds) compared to a placebo up to 3 hours after taking the dose. However, minor increases in the average QTc interval (less than 10 milliseconds) cannot be completely ruled out.
Pharmacokinetics
A study combined data from 17 trials involving both healthy individuals and cancer patients to analyze how the body processes Axitinib. The results showed that a two-compartment model with first-order absorption and a lag-time effectively explains the concentration-time profile of Axitinib drug.
Absorption and Distribution
Single 5-mg Oral Dose
- Tmax (time to highest concentration): 2.5 to 4.1 hours.
- Steady state expected within 2 to 3 days with regular dosing.
- 5 mg twice daily results in approximately 1.4-fold accumulation compared to a single dose.
- Roughly linear pharmacokinetics observed within the 1-mg to 20-mg dose range at steady state.
- Absolute bioavailability after a 5 mg oral dose: 58%.
Administration with Food
When taken with food, Axitinib can be administered with or without meals. Compared to fasting overnight, taking Axitinib with a moderate fat meal resulted in a 10% lower AUC (area under the curve), while a high-fat, high-calorie meal led to a 19% higher AUC.
Axitinib drug strongly binds to human plasma proteins (>99%), with a preference for binding to albumin and moderate binding to α1-acid glycoprotein.
In patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) receiving a 5 mg twice daily dose in the fed state, the geometric mean (CV%) Cmax and AUC0-24 were 27.8 (79%) ng/mL and 265 (77%) ng.h/mL, respectively.
The geometric mean (CV%) clearance and apparent volume of distribution were 38 (80%) L/h and 160 (105%) L, respectively.
Metabolism and Elimination
Plasma Half-life: Ranges from 2.5 to 6.1 hours for Axitinib.
Metabolism: Primarily occurs in the liver, mainly by CYP3A4/5, and to a lesser extent by CYP1A2, CYP2C19, and UGT1A1 enzymes.
Oral Administration (5-mg Dose)
- Approximately 41% of radioactivity recovered in feces.
- About 23% of radioactivity recovered in urine.
- Major component identified in feces: Unchanged Axitinib (12% of the dose).
- Unchanged Axitinib not detected in urine.
- Carboxylic Acid and Sulfoxide metabolites are the primary components in urine.
Plasma Composition
- N-glucuronide metabolite: Represents 50% of circulating radioactivity.
- Unchanged Axitinib and Sulfoxide metabolite each account for approximately 20% of circulating radioactivity.
Potency Against VEGFR-2
The Sulfoxide and N-glucuronide metabolites show >400-fold less in vitro potency against VEGFR-2 compared to Axitinib drug.
Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dose: Start with an oral dose of Axitinib 5 mg twice daily.
Administration Guidelines
- Take doses approximately 12 hours apart.
- Can be taken with or without food.
- Swallow Axitinib whole with a glass of water.
Missed Dose or Vomiting
- If a dose is missed or vomiting occurs, do not take an extra dose.
- Take the next prescribed dose at the usual time.
Common Side Effects
- Diarrhea
- Hypertension
- Fatigue
- Decreased appetite
- Nausea
- Dysphonia
- Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (hand-foot) syndrome
- Weight decreased
- Vomiting
- Asthenia
- Constipation
Drug Interactions
Metabolism: Axitinib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4/5, with additional involvement from CYP1A2, CYP2C19, and UGT1A1.
CYP3A4/5 Inhibitors
- Co-administration of strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors, like Ketoconazole, increases Axitinib plasma exposure.
- Avoid combining Axitinib with strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors.
- Grapefruit or grapefruit juice may also elevate Axitinib levels and should be avoided.
- Choose medications with minimal or no CYP3A4/5 inhibition potential. If necessary, reduce Axitinib dose when coadministering with strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors.
CYP3A4/5 Inducers
- Strong CYP3A4/5 inducers, such as Rifampin, decrease Axitinib plasma exposure.
- Avoid combining Axitinib with strong CYP3A4/5 inducers (e.g., Rifampin, Dexamethasone, Phenytoin, Carbamazepine, Rifabutin, Rifapentin, Phenobarbital, and St. John’s wort).
- Choose medications with minimal or no CYP3A4/5 induction potential.
- Moderate CYP3A4/5 inducers (e.g., Bosentan, Efavirenz, Etravirine, Modafinil, and Nafcillin) may also reduce Axitinib drug exposure and should be avoided if possible.
Warnings and Precautions
Hypertension
- Blood pressure must be well-controlled before starting Axitinib.
- Monitor and treat hypertension; reduce Axitinib dose for persistent hypertension despite medication.
Thrombotic Events
- Arterial and venous thrombotic events observed; caution in high-risk patients.
- Potential fatality; use Axitinib carefully in patients prone to such events.
Hemorrhagic Events
- Reports of hemorrhagic events, some fatal.
- Avoid Axitinib in patients with untreated brain metastasis or recent active gastrointestinal bleeding.
Cardiac Failure
- Cardiac failure observed; monitor signs or symptoms throughout treatment.
- Potential fatality; exercise caution.
Gastrointestinal Complications
- Gastrointestinal perforation and fistula, including fatal cases.
- Caution in patients at risk for these complications.
Hypothyroidism
- Hypothyroidism requiring replacement therapy reported.
- Monitor thyroid function before and during Axitinib treatment.
Surgery Precaution
- Stop Axitinib at least 24 hours before scheduled surgery.
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS)
- Permanently discontinue Axitinib if signs or symptoms of RPLS occur.
Proteinuria
- Monitor for proteinuria before and during Axitinib treatment.
- Reduce dose or temporarily interrupt treatment for moderate to severe proteinuria.
Liver Enzyme Elevation
- Elevation of ALT, AST, and bilirubin observed during Axitinib drug treatment.
- Monitor liver enzymes before and during Axitinib treatment.
Hepatic Impairment
- Decrease starting dose for moderate hepatic impairment.
- Not studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
Fetal Harm
- Axitinib can harm the fetus; caution in pregnant women.
- Women of childbearing potential should avoid pregnancy while on Axitinib.
Storage Conditions
Store in a cool and dry place, away from light. Keep out of the reach of children.
